Assembler¶
What is the OpenCloning Assembler?¶
The OpenCloning Assembler is a tool that allows you to clone with MoClo and Golden Gate kits. The best way to get a feeling of what it can do is to try it with one of the Syntaxes that are already available.
Getting started with the Assembler¶
Go to the Assembler tab and click on Load Syntax. You will see a list of available syntaxes. Click on one of them to load it. Some kits contain multiple syntaxes. For this example, we will load the MoClo YTK syntax.
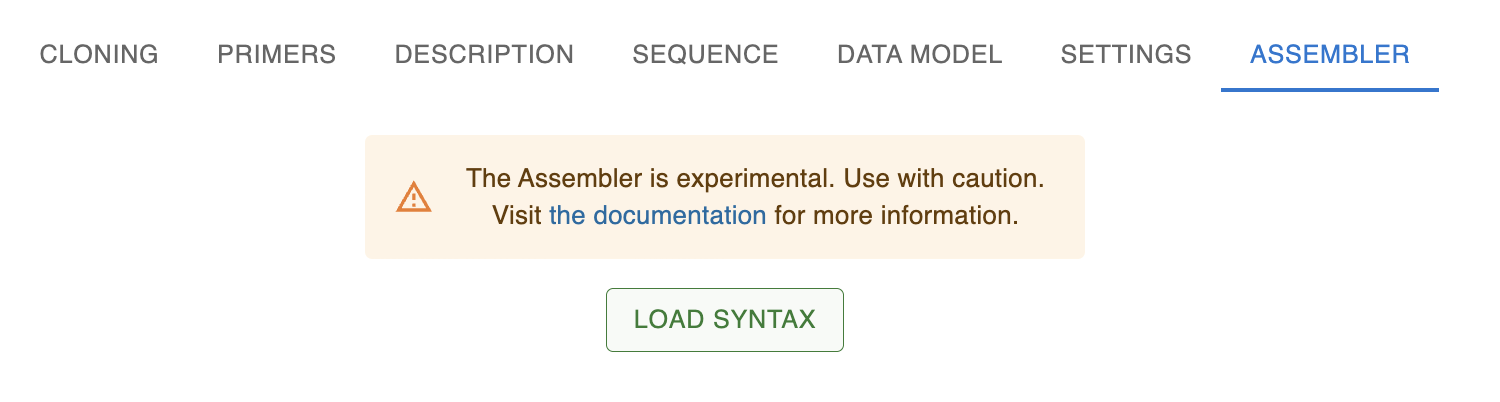
After clicking that, you should see something like this:
Loading the syntax has fetched the syntax information, as well as some sequences that are associated with the syntax, typically from an Addgene kit or similar.
In this case, all assemblies start with an Assembly connector, so the first category is already set to that. The next part in a MoClo assembly is normally a Promoter (with overhangs AACG-TATG), but there is another option available (AACG-GCTG). That is because the MoClo YTK kit contains some plasmids containing parts that span multiple overhangs. In this case AACG-GCTG, spans promoter + CDS + terminator. Even though there is not a "named category" for this, it is still picked up by the Assembler and added as an option.
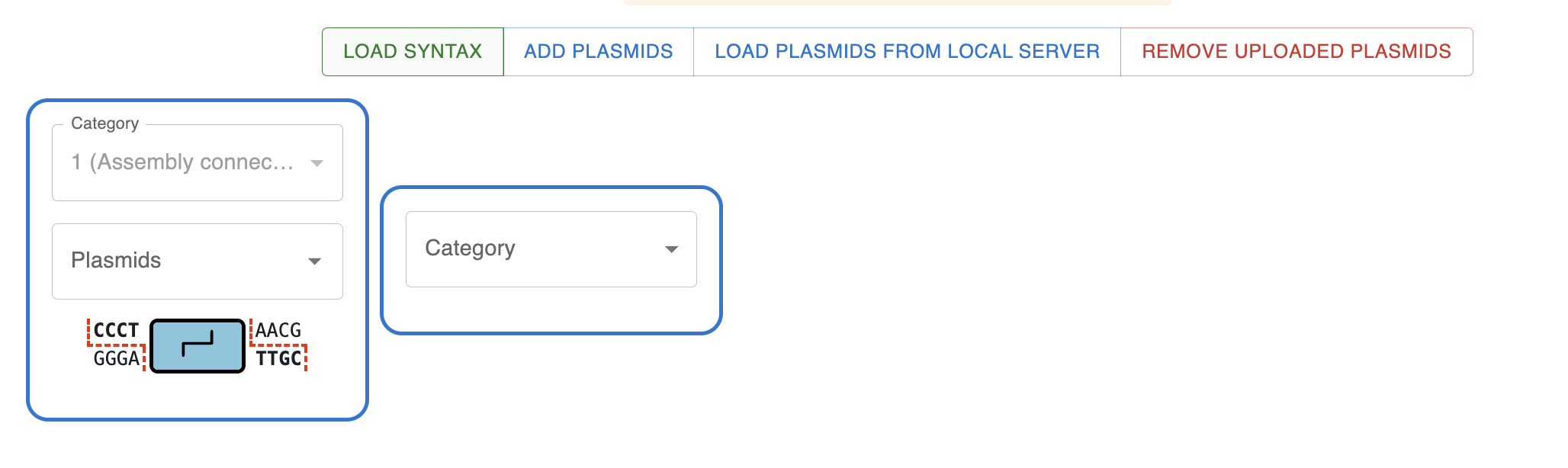
Now let's pick the "typical" assembly for a 1-CDS plasmid.
- Connector
- Promoter
- Coding sequence
- Terminator
- Connector
- Yeast marker
- Yeast ORI
- Bacterial ORI and marker
Should look like this:
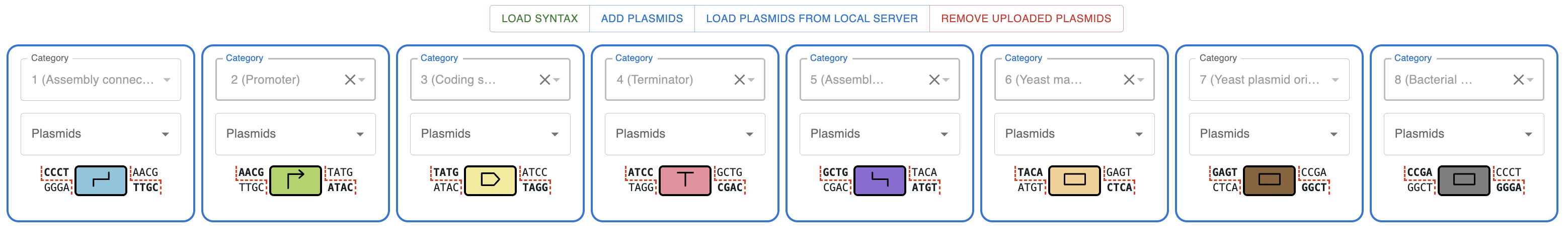
Now you can select one or more plasmids from each category. Once you have selected at least one plasmid for each category, teh Submit button will appear. Clicking it will perform the combinatorial assembly of all the possible combinations of the plasmids you selected and the results will be shown in a table.
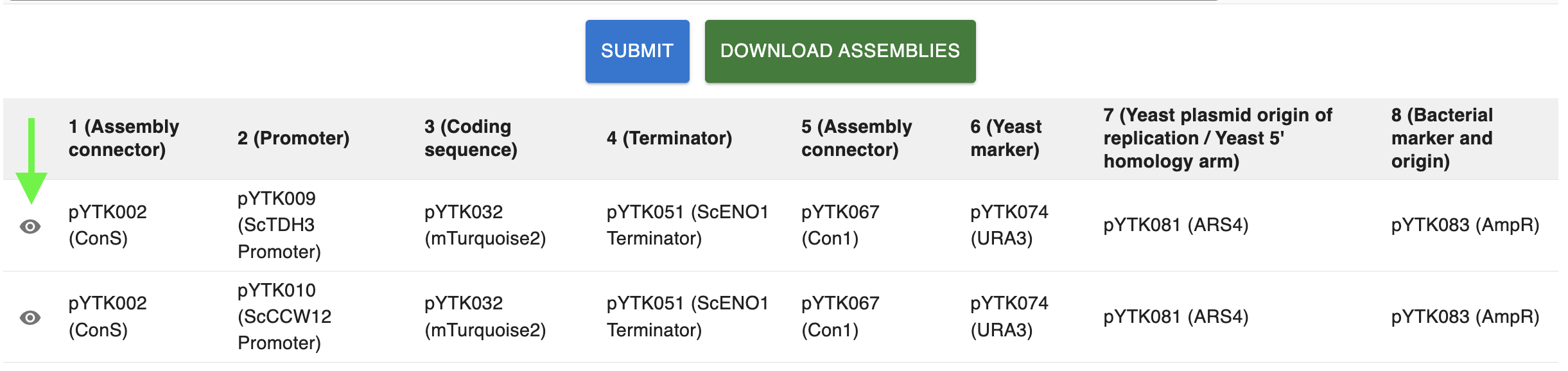
Each row in the table shows the plasmids that were assembled together for each assembly. If you click on the eye icon at the left of each row (see arrow in the image above), you will see the cloning strategy for that assembly in the Cloning tab.
Downloading the results of the Assembler¶
If you click on the Download Assemblies button at the top of the table, you will download a .zip file containing the cloning strategies for all the assemblies. The file contains:
assemblies.csvandassemblies.tsv: two tabular files containing a similar table to the one displayed in the browser, with the names of the plasmids that were assembled together for each assembly- Pairs of files with
.gband.jsonextensions for each assembly:- The file name starts with an index number, which corresponds to the row number in the table.
- The rest of the file name is the plasmids that were assembled together for that assembly, separated by
+characters. - The
.gbfile contains the sequence of the final product of that assembly. - The
.jsonfile contains the cloning strategy for that assembly.
Using your own sequences in the Assembler¶
You can use your own sequences in the Assembler by loading them from files. You can do this by clicking on the Add plasmids at the top of the Assembler tab. Once you upload the files, you will see up to two tables:
⚠️ This assumes that you are submitting plasmids, so everything will be treated as a circular sequence (e.g. if you submit fasta, or wrongly annotated genbank files).
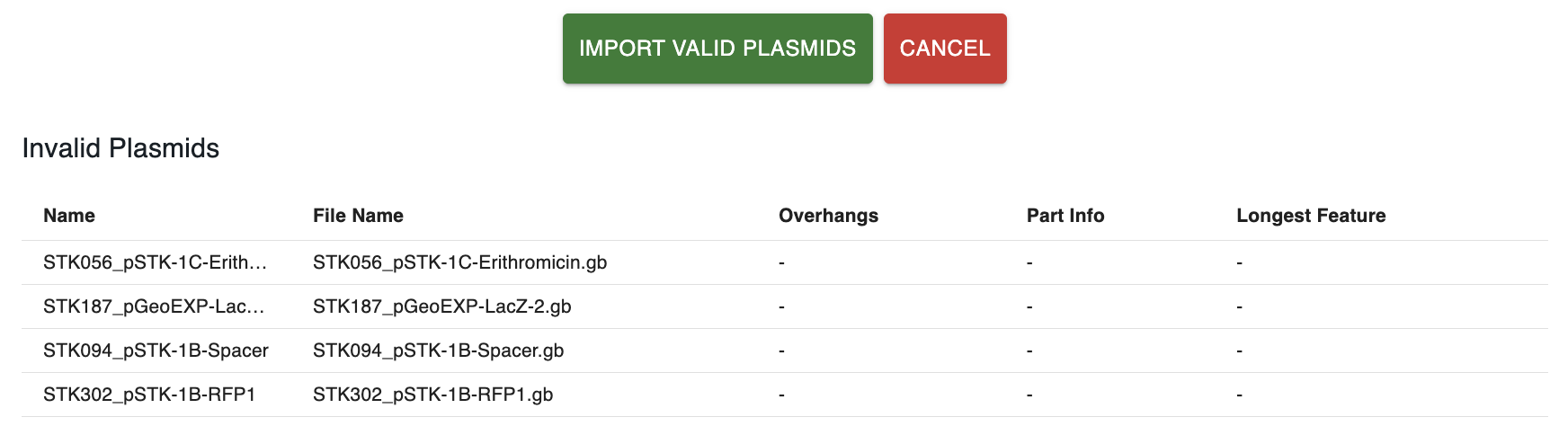
A table displaying the "invalid" sequences, those that either:
- Are not cut by the enzyme
- Do not produce overhangs compatible with the syntax when cut.
- When cut by the enzyme, produce more than one part compatible with the syntax.
This table might be missing if all the sequences are valid.
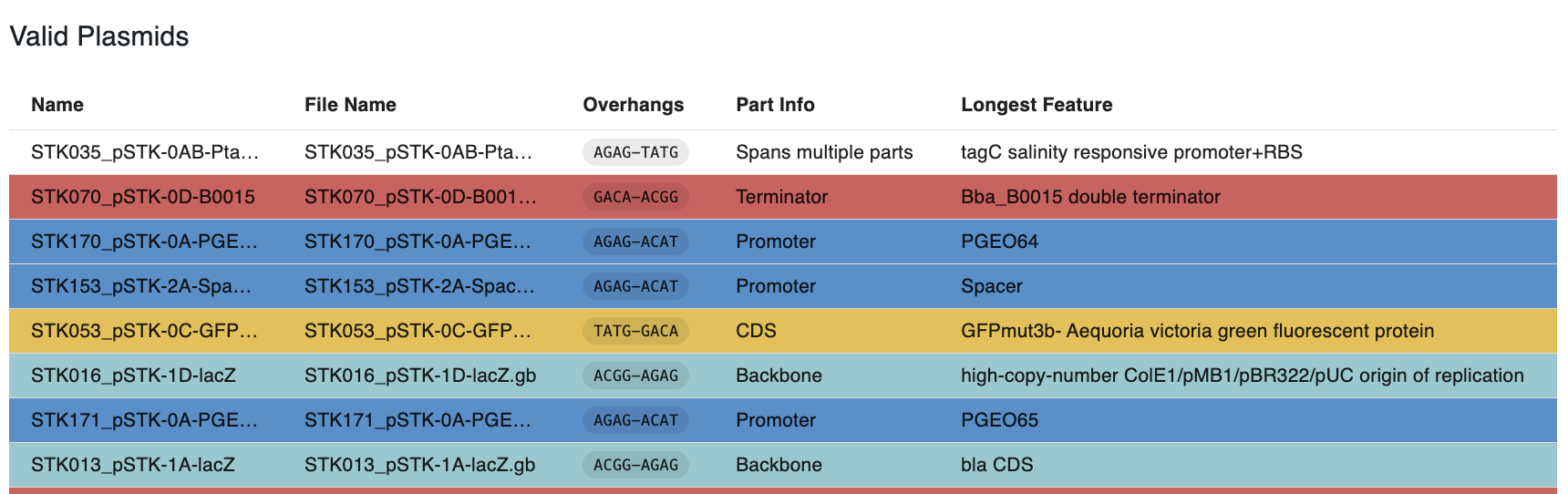
The other table displays the "valid" sequences, those that are cut by the enzyme and produce a single part with overhangs compatible with the syntax.
- They are color-coded with the color of the parts in the syntax.
- The column
Part Infodisplays the name of the part based on the syntax. - If the part spans multiple overhangs and it's not named, it will not have a color and say
Spans multiple parts. - If the sequence is annotated, the column
Longest Featuredisplays the name of the longest feature in the restriction fragment that contains the part compatible with the syntax.
If you click on Import Valid Plasmids, those plasmids will be added to the Assembler, and you will be able to select them in the categories. In the drop-downs, they will have a light green background. If you want to remove the plasmids you submitted from the Assembler, click on Remove uploaded plasmids.
Using your own syntaxes in the Assembler¶
You can create your own syntaxes in the Syntax Builder. See the documentation for more information.
Once you have created your own syntax, you can load it in the Assembler by clicking on Load Syntax and selecting Upload syntax from JSON file at the bottom of the dialog.