Oligonucleotide hybridization¶
What is oligonucleotide hybridization?¶
Two synthetic single‑stranded DNA oligonucleotides can be designed with complementary regions so that, when mixed and annealed, they form a double‑stranded DNA fragment. If each oligo has short 5' overhangs that are not complementary, the hybridized product will be a double‑stranded core with single‑stranded 5' overhangs at each end.
If a polymerase is added, it can fill in the 5' overhangs to create a fully double‑stranded product, this known as Polymerase extension of overhangs, and the combination of oligonucleotide hybridization and polymerase extension of overhangs is known as Templateless PCR.
How to plan oligonucleotide hybridization using OpenCloning¶
Unlike other cloning methods, Oligonucleotide hybridization does not require any input sequence:
- From the root
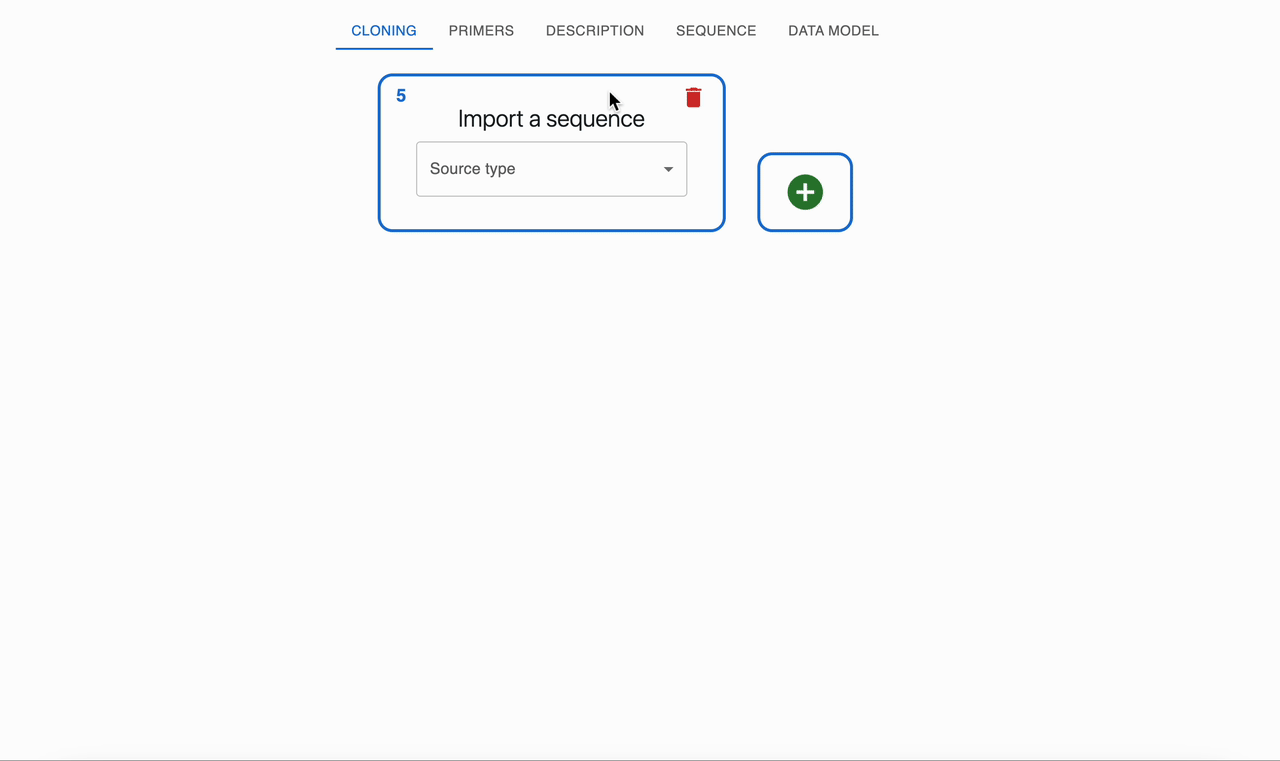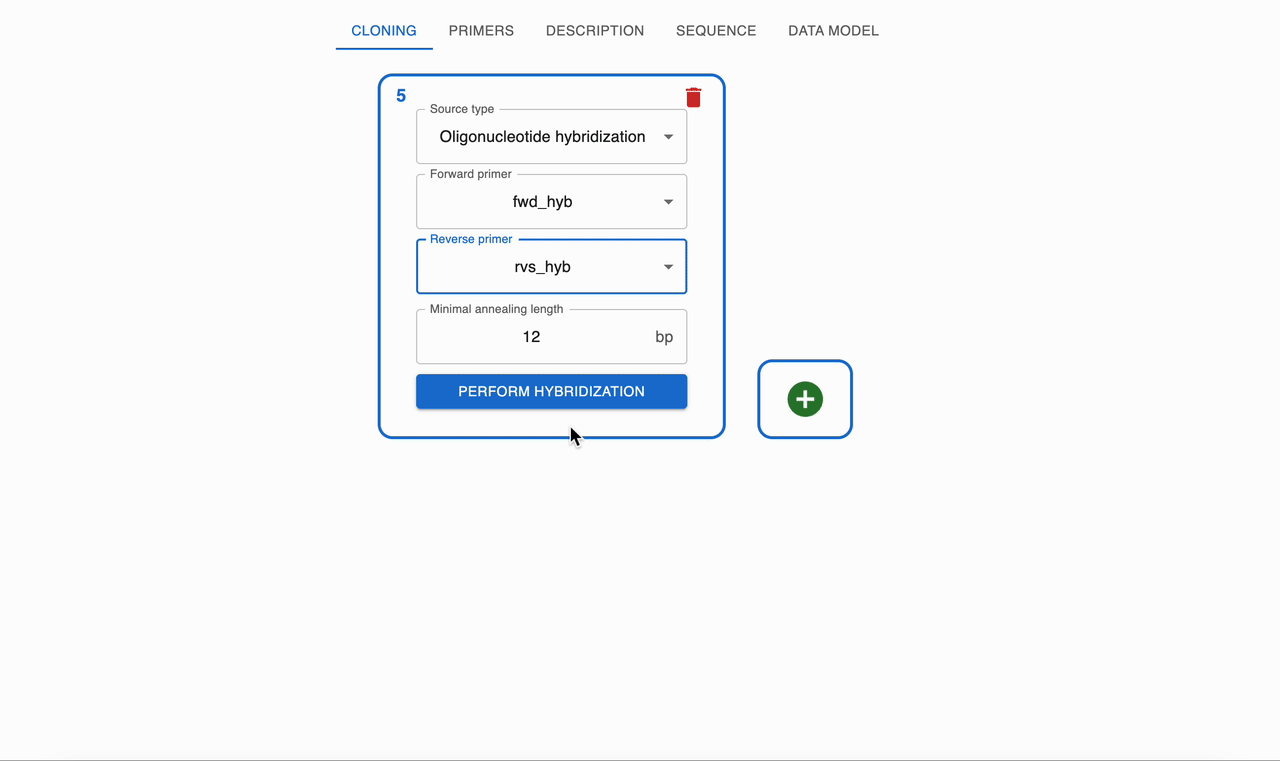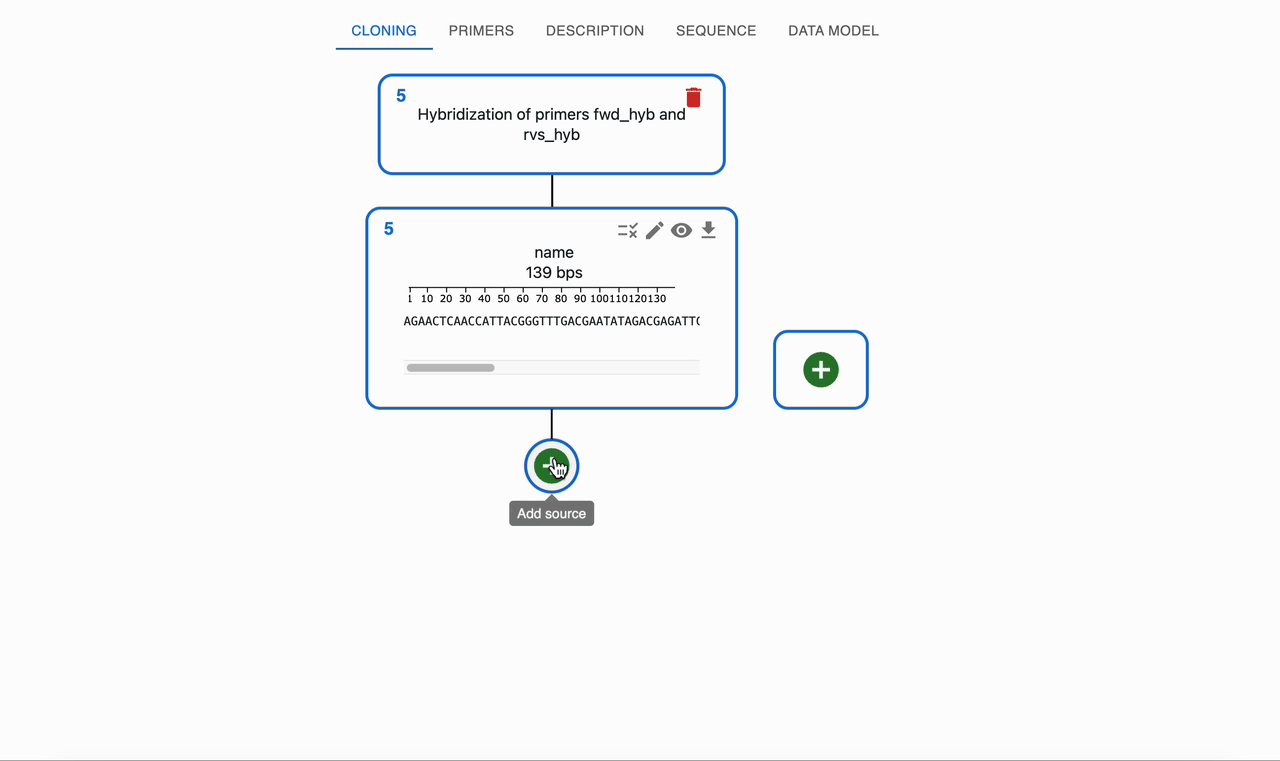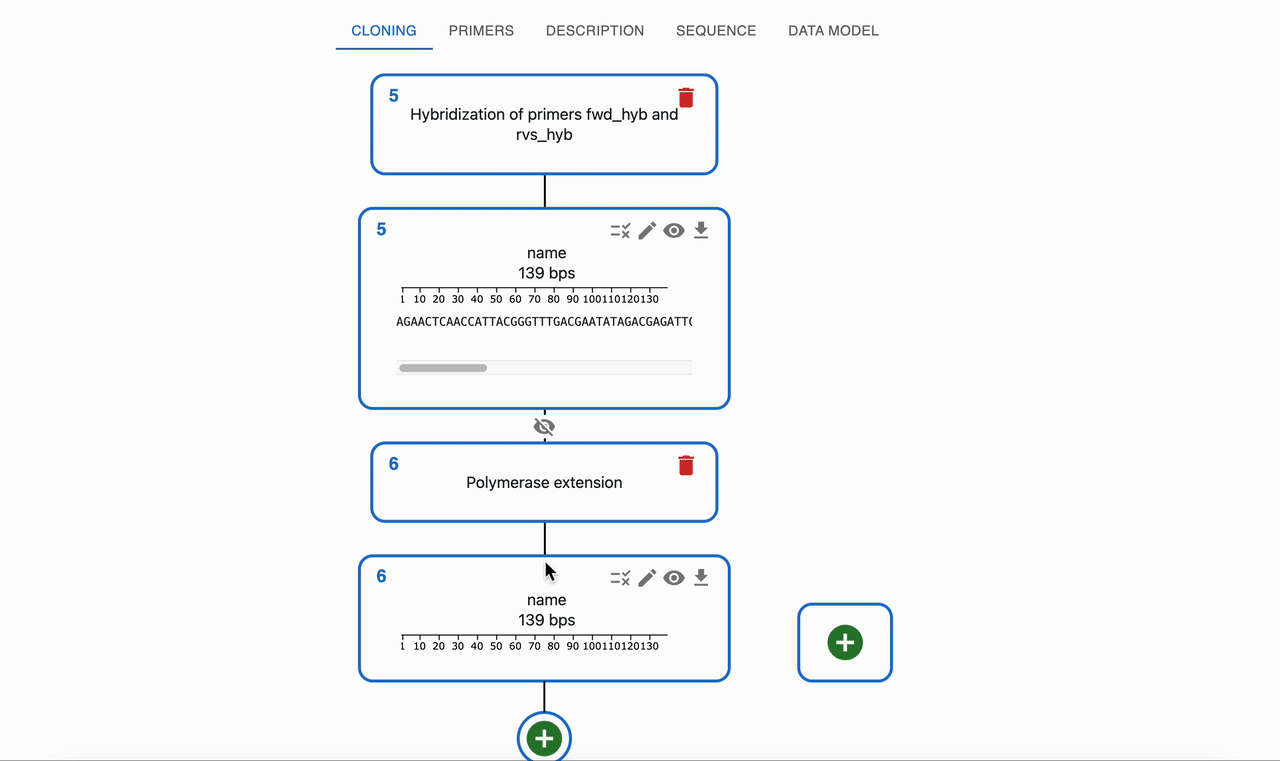
Import a Sequenceform, selectOligonucleotide hybridization. - Provide two oligos that are complementary on their 3' ends as inputs. To see how to add oligos to the session, see creating primers.
- OpenCloning simulates annealing by aligning complementary regions and reports the resulting double‑stranded product, including any remaining single‑stranded overhangs if present.